Are you wondering how to calculate the share value of a private company? Or perhaps you need to know how to calculate share price for accurate business valuations? Unlike publicly traded shares, which have readily available market prices, valuing shares in a private company is a complex process. It involves analysing financial performance, market trends, and unique company characteristics.
Join us as we explore the intricacies of private company valuation, the difference between market value vs fair value, and the role of forensic accountants in determining the true value of shares.
Private Company Valuations Explained
Do you need to know how to calculate the share value of a private company? It’s a complex process, far more intricate than the comparatively straightforward methods applied to public companies. Where public firms’ stock prices are available for all to see, private companies keep their worths’ closer to their chests, making private company valuations an often daunting process.
In business, the stakes are high, and the reasons for needing this elusive information are often diverse. Whether it’s a shareholder or business partner planning an exit, a dispute brewing among stakeholders, or the act of valuation alone has led to corporate turbulence, the need for clarity is paramount.
But fear not, there is a guiding light in the form of forensic accounting. Join us as we tackle the complexities of valuing private company shares, where the usual rules may not apply.
What is Fair Value of Shares?
The fair value of shares refers to the price a willing buyer and seller would agree upon in a transaction. Unlike market value, which is based on open market prices, fair value is influenced by specific circumstances surrounding the sale and the businesses involved. An independent valuer is often tasked with determining a fair value of shares for both parties.
When calculating the fair value of shares, the first step is often to consult the company’s articles of association. These documents may define what constitutes “fair value” in specific scenarios. However, assumptions should not be made, as this is not always the case.
The fair value of shares can also be relevant in shareholder disputes where both parties disagree on the fair value of company shares. Often in this circumstance, the figure will either be determined by what factors are deemed important by your valuer or the court, depending on the situation.
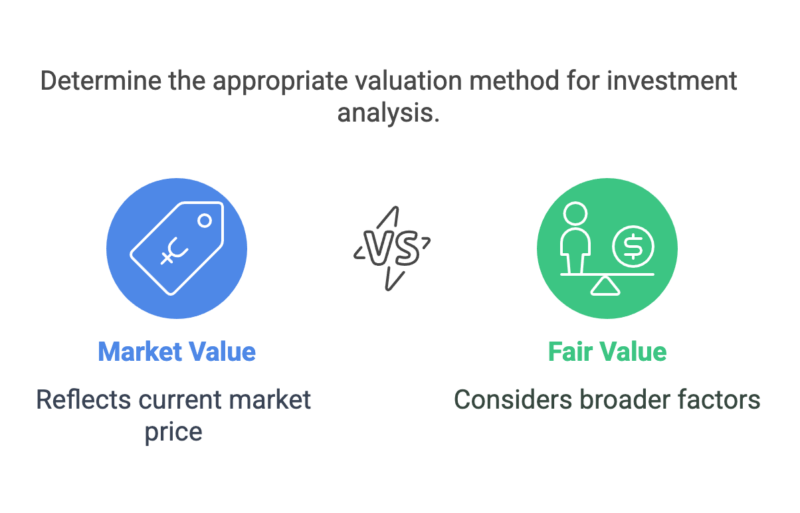
Market Value vs Fair Value of Shares
Understanding the difference between market value and fair value is crucial when learning how to calculate the share value of a private company. These two approaches to private company valuation are distinct:
- Market Value: Reflects the price a buyer would pay in a competitive and open market. For example, if a similar company in the same industry sold shares for £100 each, this could influence the market value of your shares.
- Fair Value: Takes into account broader factors, such as minority shareholders’ rights and restrictions. For instance, shares with limited voting rights may be deemed less valuable, even if their market value suggests otherwise.
Understanding these differences is essential for accurately valuing shares in a private company.
Why Is Share Valuation Important?
Share valuation is a crucial process for businesses, investors, and regulators alike. It serves an important purpose to determine the worth of a company’s shares, as well as playing a pivotal role in various financial and legal scenarios. Whether it’s for mergers and acquisitions, tax purposes, or resolving a dispute, accurate share valuation ensures fairness, transparency, and informed decision-making.
Here are some of the key reasons why share valuation is so important in the UK:
- Mergers and Acquisitions: In M&A transactions, share valuation ensures fair pricing for both parties.
- Investor Decision-Making: For investors, share valuation is important for evaluating whether stocks are over, under, or fairly priced.
- Dividends and Earnings: Accurate share valuation helps firms determine how profits should be distributed among shareholders.
- Resolve Shareholder Disputes: Valuation can be key in resolving shareholder disputes, particularly in buyout or exit scenarios. It provides a solid basis to determine a fair price that shares should be sold or purchased at.
- Track Performance: Share valuation serves as a vital indication of a company’s performance. It helps key stakeholders to track the company’s financial health and long-term growth.
- Business Valuations: Share valuations are also critical for businesses, during times of ownership transfer, restructuring, or determining fair inheritance split in order to contribute to an accurate valuation.
Accurate private company valuation is also vital in resolving shareholder disputes, where parties may disagree on the fair value of shares.
How Do I Calculate the Value of My Shares?
Working out how to calculate the share value of a private company can be complex. Unlike public firms, private businesses lack readily available stock prices. The process of calculating share value of private firms often involves methods like Comparative Company Analysis and Discounted Cash Flow valuation, considering industry benchmarks and cash flow projections, to arrive at a fair share value.
Valuing private shares can be an important step in resolving a shareholder dispute, and understanding the key methods can be vital. The two primary methods to calculate the share value of a private company are:
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) valuation is one of the more widely used methods for share valuation of a private company.
This particular method aims to formulate a value based on expected future cash flow. The goal of DCF is to estimate the current share value of a business based on projections of how much income it could generate in the future.
The purpose of DCF as a method is to estimate the possible future return on an investment, taking into account the time value of money, which states that money today is worth more than the same money in the future because, if it is invested today, it will theoretically be worth more tomorrow.
When it comes to DCF, the main drawback is that it relies heavily on assumptions. It requires as accurate estimates as possible, despite the market being prone to fluctuation, which then affects future share value.
Factors that could affect future cash flow include:
- Falling/rising demand
- Increasing/decreasing industry competition
- Economic health
- Future innovations
- Disruption
Comparable Company Analysis
Comparable company analysis is one of the most straightforward methods for valuing shares in a private company. It involves:
- Identifying similar companies in the same industry.
- Analysing their financial metrics and performance.
- Using valuation ratios (e.g., P/E ratio, EBITDA multiples) to estimate the value of shares.
An expert, such as a forensic accountant, can compile a list of comparable businesses and analyse their statistics to determine an average valuation.
How Do You Value Shares in a Private Company: Practical Steps
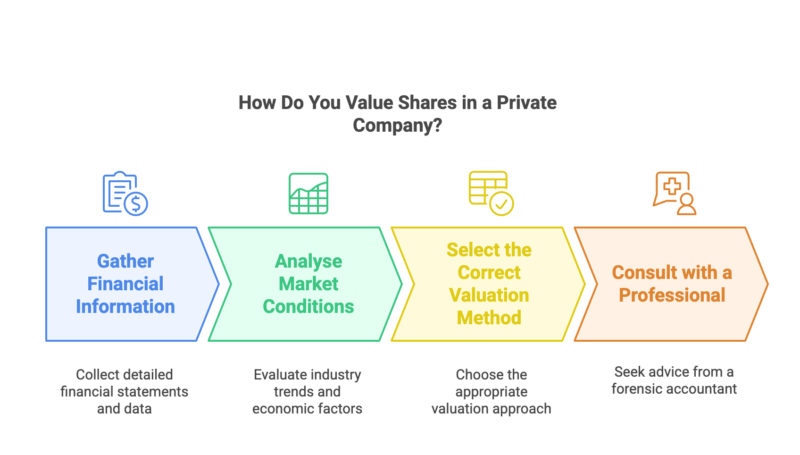
Valuing shares in a private company involves a detailed process of gathering financial data, analysing market conditions, selecting the appropriate valuation method, and adjusting for factors like minority discounts. This step-by-step guide outlines the key stages to ensure a fair and accurate company valuation.
- Gather Financial Information: The first and most important step is to collect accurate and detailed financial statements. It’s also helpful to gather historical financial data as well as forecasted financial statements. This should include:
- Balance Sheets
- Profit and Loss Accounts
- Cash Flow Statements
- Analyse Market Conditions: Assessing external factors can be critical, as they can have a significant impact on valuation. Areas to evaluate include:
-
- Industry trends
- Economic climate
- Regulatory changes
- Select the Correct Valuation Method: Choosing the appropriate valuation method is vital for achieving a fair and accurate assessment.
- Consult with a Professional: While the steps provided act as a foundation for the valuation process, it can be complex and highly subjective. Consulting with a forensic accountant can ensure that the valuation is thorough and accurate, while aligning with the latest standards.
Factors Affecting the Value of Shares
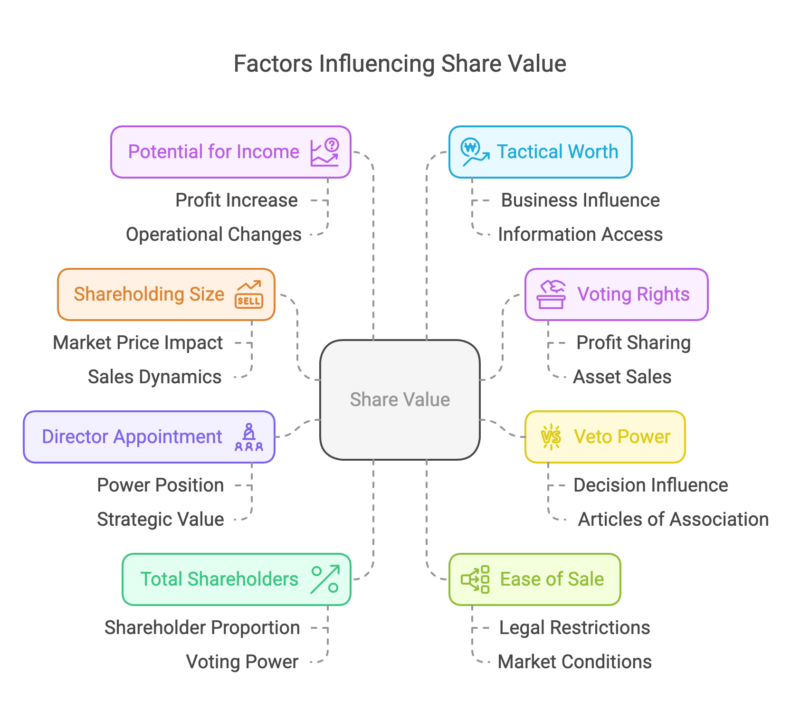
To properly answer the question, “How do I calculate the value of my shares?” it can be useful to delve deeper than valuation. A number of other factors, including shareholding size, veto rights, and business plans, can also have an impact. Effectively, the better you understand the wider picture, the more accurate the valuation is likely to be.
Some of the more common factors to look out for include:
- Shareholding Size: Sales within a bigger shareholding could affect the overall market price, which could lead to the price coming down.
- Voting: Voting rights affect your ability to make key decisions, such as profit sharing and asset sales. Therefore, increased voting rights are regarded as being more valuable.
- Veto: Depending on the contents of articles of association, shareholders with 25% (or less) of total shares could have ample power to veto decisions.
- Right to Appoint a Director: The ability to appoint a director puts a shareholder in a more powerful — and therefore valuable — position.
- Total Shareholders: The proportional makeup of the shares is critical, as being a 10% shareholder would carry more weight if nine other people also owned 10% — as everyone would have an equal say. This would make your investment much more valuable than if two other people owned the remaining 90%.
- Ease of Sale: Another important factor for anyone wondering, “How do I value my shares?” is how easily they could eventually be sold. This will be influenced by any legal restrictions on the mechanism for selling, with limitations tending to reduce share value.
- Potential for Income: Any expected increase in profits — due to a new service, or change of operations — could significantly boost share value.
- Tactical Worth: Even a minority shareholding could theoretically influence the future of a business. It might even offer access to information that could be of strategic importance. In short, the greater a share’s influence and access, the more valuable the investment could be at sale.
These factors, along with the company’s articles of association, play a crucial role in determining the fair value of shares.
How to Calculate the Share Value of a Private Company: Common Challenges
Valuing shares in a private company can be challenging due to limited market data, subjective assumptions, and a lack of liquidity. These factors make it difficult to establish an accurate share value. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for achieving a fair and reliable company valuation.
Common challenges include:
- Limited Comparables: Unlike public companies, private firms don’t have easily accessible market comparables.
- Subjective Assumption: Many common methods of valuation rely on some level of assumption, such as projected growth rates or discount rates, which can vary based on who is conducting the appraisal.
- Lack of Liquidity: Private company shares may have less liquidity, which can impact their perceived value in comparison to publicly traded shares.
Addressing Challenges
To overcome these challenges it’s important to utilise multiple methods of valuation in order to triangulate the fairest value. It’s also recommended that you regularly update your valuation in order to reflect any market or company changes, as well as ensure you work with an experienced professional with an understanding of best practices when it comes to the understanding of private company valuations.
How to Calculate Share Value and Share Price
Here are some frequently asked questions about how to calculate the share value and how to calculate share price:
What is the Best Method to Calculate Share Price?
The best method depends on the company’s specifics. Comparable Company Analysis (CCA) is ideal for benchmarking, while Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) is better for future cash flow projections.
How do I Calculate the Share Value of a Private Company?
To calculate the share value, gather financial data, analyse market conditions, choose a valuation method (e.g., CCA or DCF), and consult a professional for accuracy.
Can I Calculate Share Price Without Professional Help?
While it’s possible to estimate share price using financial data and valuation methods, consulting a forensic accountant ensures accuracy and reliability.
How Forensic Accounting Helps with the Calculation of Fair Value of Shares
No matter whether it is being done to enable a business sale/buyout, or to end a shareholder dispute, knowing how to calculate the share value of a private company can be a particularly complicated and involved process.
The last thing anybody wants is for a valuation to be made, and it be grossly under or overvalued, leading to an inflated/under inflated valuation that could cause major issues.
An experienced forensic accountant has all the skills required to accurately and efficiently assess the share value of a private company, while providing clarity and calm throughout the process.
Why Work with Inquesta Forensic When Calculating the Value of Shares
If you’re wondering how to calculate the share value of a private company, Inquesta Forensic offers expert assistance. Our team specialises in:
- Accurate Valuations: Using proven methods like CCA and DCF.
- Comprehensive Analysis: Leaving no stone unturned to provide precise valuations.
- Client-Focused Service: Tailored to meet your specific needs.
Our specialist team has been carefully and deliberately assembled to provide the best service available, with experts capable of assisting you in all manner of needs; from calculating share value, to forensic insolvency, commercial dispute, and more.
Calculating the fair value of shares in a private company can be a complicated process at times, particularly for those without experience in the matter.
We know and understand all of the subtle complexities and data difficulties that can arise in the process. Decades of experience helping businesses means that we are perfectly placed to provide you an excellent service that can get you the best result.
The Inquesta team will conduct a thorough and detailed investigation, leaving no stone unturned and no document unread, in order to put forward the most accurate valuation possible.
Instructing a forensic accountant with Inquesta guarantees a service that covers all bases for you and is designed from the ground up with our clients in mind.
Contact our team, request a free consultation today, and learn more about what we can do to assist you.
- Cryptocurrency Valuation During Divorce When Bitcoin Crashes: The Impact of Timing and Volatility
- Your Partner’s Been Convicted: Can They Take Your House? What Section 10a POCA Means For You
- The Essential Role of Forensic Accounting in High Net Worth Divorce
- How to Value a Startup Business: A Guide for UK Entrepreneurs
- Pig Butchering Scams: Guide to Crypto Romance Fraud